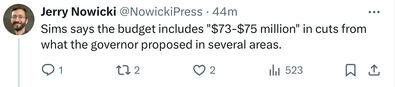|
Good stuff (Updated x1)
Sunday, May 26, 2024 - Posted by Rich Miller * Peter Hancock at Capitol News Illinois has been ably following the governor’s proposed health insurance changes this spring and the last time I saw him at a Pritzker press conference, he asked very informed questions. His latest from yesterday…
Go read the rest. You can read all of Hancock’s stories here. * Meanwhile, WAND TV reporter Mike Miletich has been killing it lately. Dude is churning out multiple informative stories a day. One from yesterday…
Click here to read what he’s been writing. * Blog favorite Tina Sfondeles is back in Springfield to cover the rest of the session. Excerpt from her latest…
* I met Tribune reporter Olivia Olander for the first time yesterday. Her informative story on the governor’s health insurance reform package today is definitely worth a read. Excerpt…
* Another blog favorite, Capitol News Illinois reporter Hannah Meisel, is also a must-follow on Twitter…
Hannah then linked to this helpful story…
…Adding… Update…  * I’m sure I’ve missed some solid stuff in this post. For instance, Jerry Nowicki of Capitol News Illinois has been tweeting out lots of Statehouse info. Make sure to click here and follow the whole show with our live session coverage.
|
|
Session updates (Updated x3)
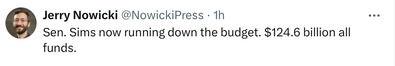
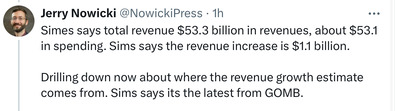
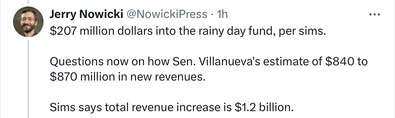
Sunday, May 26, 2024 - Posted by Isabel Miller * Jerry Nowicki‘s recap of the Senate Appropriations hearing this morning… * Sen. Sims said there will likely be a third amendment to the budget introduced on the floor. The budget’s bill number is SB251….
* The BIMP will be moved to HB4959, SA2, though language has not yet been introduced as I write this. …Adding… Subscribers were told more about yesterday’s House member deficit early today…
What Harmon said yesterday in response to my question before the House adjourned…
…Adding… Al Llorens, president of the Illinois Education Association…
…Adding… Click here to follow developments as they happen… 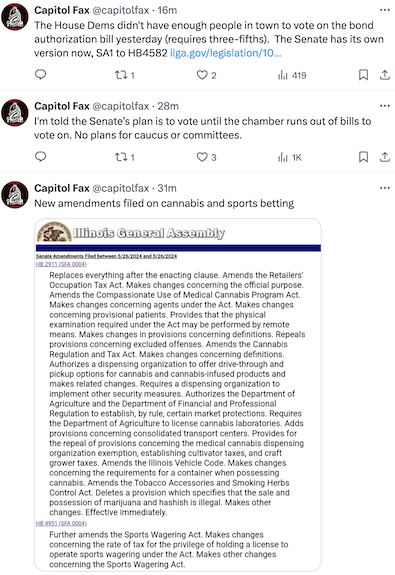
|
|
*** 2024 end of session cheat sheet ***
Sunday, May 26, 2024 - Posted by Isabel Miller * FY25 Approp bill - SB251, SA3 * Revenue omnibus - HB4951, SA2, SA3, SA4, SA5 * Use Tax Act Omnibus (Eliminates grocery tax) - HB3144, SA2, SA3 * Bonding Authority - HB4582, SA1 * Tax incentives, credits - HB5005 * Procurement omnibus - HB5511 * Medical Debt Relief Act - HB5290 * Cannabis omnibus - HB2911 (Senate floor amendments filed) * Hemp Consumer Products Act - HB4293 * Prisoner Review Board reform - HB681 SFA5 * Repeals sub-minimum wage for persons with disabilities - HB793 (Senate First Reading) * Prevents hospital patient abuse - HB587 (Senate First Reading) * Family Amusement Wagering Prohibition Act - SB327, House Amendment 1 * Healthcare Protection Act - HB5395 * Short Term Insurance Ban - HB2499 * Birth equity - HB5142 * Election omnibus - HB4488 * Worker Freedom of Speech Act - SB3649 * Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) - SB1289 * Medicaid Omnibus - SB3268, HFA2
|
|
*** LIVE session coverage ***
Sunday, May 26, 2024 - Posted by Isabel Miller * Click here for our end of session cheat sheet…
|
|
Live coverage
Sunday, May 26, 2024 - Posted by Rich Miller * You can click here or here to follow breaking news. It’s the best we can do unless or until Twitter gets its act together.
|
| « NEWER POSTS | PREVIOUS POSTS » |